The textile and fashion industry is one of the most polluting and wasteful industries in the world. Every year, more than 100 billion items of clothing are produced, but only a fraction of them are reused or recycled. The rest end up in landfills, incinerators, or oceans, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, water pollution, and resource depletion. How can we reduce the environmental impact of fashion and make it more circular? One of the most promising solutions is textile recycling, which involves turning old textiles into new fibers or products. Textile recycling can save energy, water, and raw materials, while creating new opportunities for innovation and employment. In this article, we will explore the current state of the textile recycling industry, its trends, challenges, and opportunities, and its future outlook.
What is Textile Recycling?
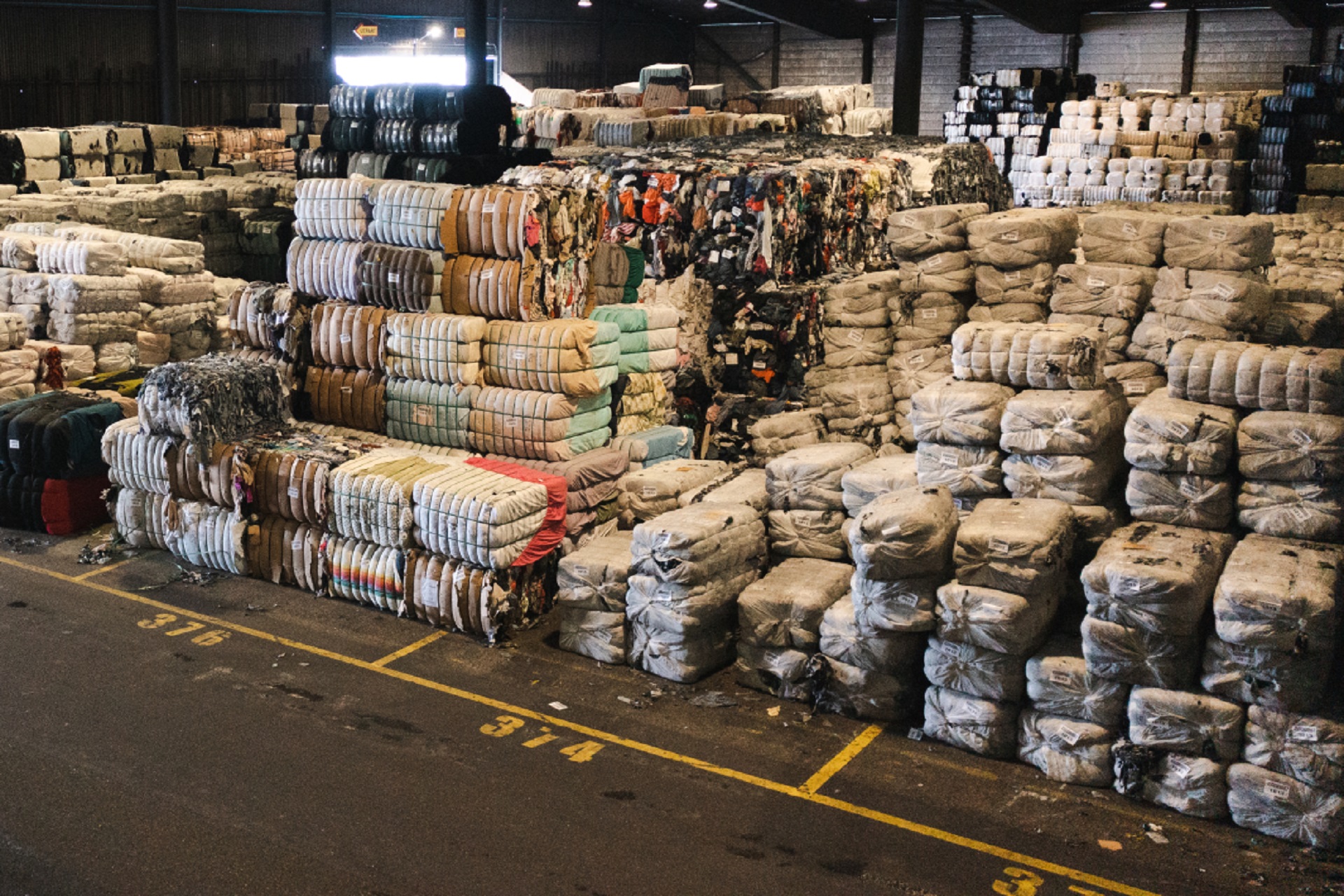
Textile recycling is the process of taking textiles that are no longer in use and giving them new life. Textile products include all items made from cloth, such as clothing, bed linens, and towels, etc. Recycling can involve:
- Downcycling, which turns textiles into products with lower value, such as rags, insulation, or stuffing.
- Upcycling, which turns textiles into products with higher value than the original product which is being recycled
- Textile-to-textile recycling, which creates new textiles or garments from the fibers of old ones.
Textile recycling can be done in two ways:
- Mechanical recycling, which involves the manual shredding of textiles and pulling them apart into their fibers followed by their conversion to useful products.
- Chemical recycling, which involves dissolving textiles into their molecular components and then regenerating them into new fibers. This method is more recent and can also handle cotton as well as synthetic materials like polyester or nylon.
Textile recycling is a step taken by the fashion industry to reduce its harmful impact on the environment. According to a report by McKinsey, textile recycling could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 56%, water consumption by 79%, and energy consumption by 66% compared to virgin fiber production.
What are the Trends in Textile Recycling?
Textile recycling is a fast-growing and innovative sector that is attracting attention from various stakeholders. Some of the trends in textile recycling are:
- Increasing consumer awareness and demand. Consumers are becoming more conscious of the environmental and social costs of fashion and are looking for more sustainable alternatives. According to a survey by GlobalData, 69% of consumers in 2020 said they were interested in buying clothes made from recycled materials, up from 57% in 2019.
- Rising regulatory pressure. Governments are introducing policies and regulations to encourage textile recycling and discourage textile waste. For example, in 2020, France banned the destruction of unsold clothes and imposed mandatory collection schemes for retailers. In 2021, the UK introduced an extended producer responsibility scheme that requires producers to pay for the collection and disposal of their products.
- Growing industry collaboration. Fashion brands, retailers, manufacturers, recyclers, NGOs, and researchers are working together to develop and scale textile recycling solutions. For example, in 2020, H&M launched a garment-to-garment recycling system called Looop in its Stockholm store. The system allows customers to bring their old clothes and watch them being transformed into new ones in front of their eyes.
- Advancing technology development. Textile recycling technologies are evolving rapidly and becoming more efficient, scalable, and versatile. For example, Renewcell, a Swedish company that uses chemical recycling to turn textile waste into new fibers called Circulose®, opened the world’s first commercial-scale textile-to-textile chemical recycling pulp mill in 2023. The company aims to recycle the equivalent of more than 1.4 billion T-shirts every year by 2030.
What are the Challenges in Textile Recycling?
Despite its potential benefits and opportunities, textile recycling faces several challenges that need to be overcome to reach its full scale and impact. Some of the challenges are:
- Low collection rates. The first step in textile recycling is to collect the textile waste from consumers or businesses. However, according to McKinsey1, only 30% to 35% of textile waste is collected on average in Europe, while the rest is thrown away or exported outside Europe.
- Complex sorting and preprocessing. The second step in textile recycling is to sort and preprocess the textile waste according to the input requirements of different recycling technologies. However, most textiles are made of mixed materials or contain impurities such as buttons, zippers, or elastane. These need to be identified and removed before recycling, which is a labor-intensive and costly process. Advanced, accurate, and automated fiber sorting and preprocessing technologies are not yet widely available or affordable.
- Limited technology maturity and quality. The third step in textile recycling is to turn the textile waste into new fibers or products using mechanical or chemical recycling technologies. However, most of these technologies are still in the development or pilot stage and have not reached commercial scale or profitability. Moreover, some of these technologies have limitations in terms of the quality, durability, or color of the output fibers or products, which may affect their market acceptance and demand.
What are the Opportunities in Textile Recycling?
Textile recycling offers many opportunities for the fashion industry and beyond. Some of the opportunities are:
- Creating new value streams. Textile recycling can create new value streams for the fashion industry by turning waste into a resource. For example, according to McKinsey1, fiber-to-fiber recycling could generate €2 billion to €3 billion in revenues by 2030 in Europe alone. Moreover, textile recycling can create new markets and products for other industries, such as automotive, construction, or agriculture, that can use recycled textiles as inputs or outputs.
- Driving innovation and differentiation. Textile recycling can drive innovation and differentiation for the fashion industry by enabling new designs, materials, and business models. For example, Adidas launched a line of shoes made from recycled ocean plastic in collaboration with Parley for the Oceans, a nonprofit organization that raises awareness about ocean pollution. The shoes have been a success among consumers and have won several awards for sustainability and innovation.
- Enhancing social and environmental impact. Textile recycling can enhance the social and environmental impact of the fashion industry by reducing its negative externalities and creating positive outcomes. For example, textile recycling can create new jobs and income opportunities for workers in the recycling sector, especially in developing countries where textile waste is abundant. Moreover, textile recycling can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, and energy consumption associated with virgin fiber production, as well as prevent textile waste from polluting landfills, incinerators, or oceans.
Who are the key players in recycling?
Textile recycling is a diverse and dynamic industry that involves many players from different sectors and regions. Some of the key players in textile recycling are:
Renewcell
- Renewcell is a Swedish company that produces Circulose, a high-quality recycled textile fiber made from chemically recycled cotton and viscose. Renewcell operates the world’s first commercial-scale textile-to-textile chemical recycling mill in Sundsvall, Sweden, which can recycle up to 60,000 tons of textile waste per year. Renewcell has partnered with several fashion brands, such as H&M, Levi’s, and Asos, to use Circulose in their products.
Worn Again Technologies
- Worn Again Technologies is a UK-based company that develops a chemical recycling technology that can separate, decontaminate, and extract polyester and cellulose from mixed-fiber textiles. Worn Again Technologies aims to create a circular resource network that connects textile waste suppliers, recyclers, and manufacturers. Worn Again Technologies has received support from several investors and partners, such as H&M, Kering, Sulzer Chemtech, and Unilever.
Evenu
- Evrnu is a US-based company that creates NuCycl, a patented fiber engineering technology that transforms textile waste into high-performance fibers. NuCycl can handle various types of textile waste, such as cotton, polyester, or blends, and create fibers with customized properties, such as stretch, strength, or softness. Evrnu has collaborated with several fashion brands, such as Adidas, Levi’s, and Stella McCartney, to create products using NuCycl.
I:CO
- I:CO is a global service provider for collection, reuse, and recycling of used clothing and shoes. I:CO operates a network of more than 60 countries and collects more than 1.5 million kilograms of textiles per day. I:CO sorts the collected textiles into different categories according to their condition and potential for reuse or recycling. I:CO also offers solutions for circular design, product stewardship, consumer engagement, and social impact.
Bank & Vogue
- Bank & Vogue is a Canadian company that specializes in the wholesale trade of used clothing and other goods. Bank & Vogue sources used clothing from various channels, such as charity shops, thrift stores, or retailer take-back schemes. Bank & Vogue then sells the used clothing to different markets around the world, such as second-hand retailers, rag graders, or fiber recyclers. Bank & Vogue also operates Beyond Retro, a vintage clothing retailer with stores in the UK and Sweden.
What is the outlook for recycling?
- Consumer behavior and demand. Consumer behavior and demand will play a crucial role in driving or hindering the growth of textile recycling. Consumers need to be aware of the environmental and social impacts of fashion and be willing to change their consumption habits. Consumers also need to be satisfied with the quality, price, availability, and variety of recycled products. Consumer behavior and demand will depend on factors such as education, awareness, incentives, preferences, trends, or values.
- Technological innovation and development. Technological innovation and development will play a key role in improving the efficiency, quality, and scalability of textile recycling. Technology needs to address the challenges and limitations of textile recycling, such as low collection rates and quality, high costs and low profitability, and lack of standards and regulations. Technology also needs to create new opportunities and markets for textile recycling, such as new products, applications, or sectors. Technological innovation and development will depend on factors such as research, investment, collaboration, or regulation.
- Regulatory policies and initiatives. Regulatory policies and initiatives will play an important role in supporting or hindering the growth of textile recycling. Policies and initiatives need to create a favorable and conducive environment for textile recycling, such as providing subsidies, incentives, or funding, setting targets, standards, or regulations, or facilitating cooperation among stakeholders. Policies and initiatives also need to address the challenges and risks of textile recycling, such as environmental or social impacts, fraud or greenwashing, or trade barriers. Regulatory policies and initiatives will depend on factors such as political will, public opinion, or international cooperation.
What are the current events or future developments that could impact recycling?
Textile recycling is a dynamic and evolving industry that is influenced by various events or developments that could have positive or negative impacts on its growth and performance. Some of the current events or future developments that could impact textile recycling are:
- Climate change. Climate change is a global challenge that affects the fashion industry and textile recycling. On one hand, climate change poses a threat to the availability and quality of natural resources and raw materials for textile production and recycling, such as water, land, energy, or crops. On the other hand, climate change also creates a motivation and urgency for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating environmental impacts through textile recycling. Climate change also creates a need and demand for more resilient and adaptive textiles that can cope with changing weather conditions.
- Social movements. Social movements are collective actions that aim to achieve social or political change in society. Social movements can affect the fashion industry and textile recycling by influencing consumer behavior and demand, public opinion and awareness, or regulatory policies and initiatives. For example, social movements such as Black Lives Matter, Me Too, or Extinction Rebellion can raise awareness and demand for diversity, inclusion, equality, or environmental justice in fashion and textile recycling. Social movements can also pressure or challenge the fashion industry and textile recyclers to be more transparent, accountable, and responsible for their social and environmental impacts.
Conclusion
Textile recycling is a vital and viable solution for the fashion industry’s colossal waste problem. It can save natural resources, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, create jobs, and generate revenue. Textile recycling can also support social responsibility and circular economy in fashion. However, textile recycling also faces many challenges and uncertainties that need to be overcome to reach its full potential. Textile recycling also offers many opportunities and possibilities for innovation, growth, and impact in the fashion industry. It is influenced by various factors, such as consumer behavior and demand, technological innovation and development, regulatory policies and initiatives, or current events or future developments. Textile recycling is a promising and growing industry that has the potential to transform the fashion industry and create a more sustainable and circular future.