Cotton is one of the most widely used natural fibers in the fashion industry. However, the production of conventional cotton has several environmental problems, including the use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers that deplete the soil and damage it, high CO2 emissions, and water pollution. To address these issues, some companies are turning to more sustainable cotton options, such as organic cotton, recycled cotton, and regenerative organic certified cotton.
Regenerative Organic Certified™ (ROC) Cotton is a type of cotton that is grown using regenerative agriculture practices that aim to improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and sequester carbon. The Regenerative Organic Alliance is the main certification that ensures the use of regenerative agriculture practices for cotton. This certification goes beyond organic certification and includes requirements for soil health, animal welfare, and social fairness.
Patagonia, a clothing company known for its commitment to sustainability, has been using ROC Cotton in its products. They piloted their first crop of cotton on more than 150 farms working toward Regenerative Organic Certification. Patagonia also uses organic cotton, recycled cotton, and Cotton in Conversion, which comes from farmers who are transitioning their crops from conventional to organic cotton.
ROC Cotton has several benefits over conventional cotton. It helps to improve soil health, increase biodiversity, and sequester carbon. It also promotes social fairness and animal welfare. By supporting regenerative agriculture practices, ROC Cotton can help to mitigate the environmental problems caused by conventional cotton production.
While organic cotton has limitations, ROC Cotton offers a more sustainable option for cotton production. However, it is important to note that ROC Cotton is still a relatively new certification, and there is limited availability of ROC Cotton products on the market. As more companies adopt regenerative agriculture practices, we may see an increase in the availability of ROC Cotton products in the future.
What are the environmental benefits of regenerative organic certified cotton?
Regenerative Organic Certified™ (ROC) Cotton has several environmental benefits over conventional cotton. Here are some of the environmental benefits of ROC Cotton:
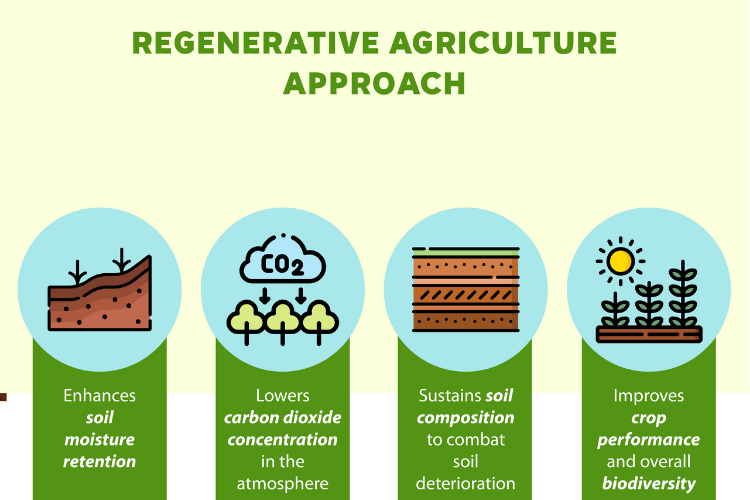
- Improves Soil Health: Regenerative agriculture practices used to grow ROC Cotton aim to improve soil health by increasing soil organic matter, reducing soil erosion, and enhancing soil fertility. This helps to maintain the soil’s ability to support plant growth and sequester carbon.
- Increases Biodiversity: Regenerative agriculture practices used to grow ROC Cotton aim to increase biodiversity by promoting the growth of different crops and plants, which in turn attracts a variety of insects and animals. This helps to create a more balanced ecosystem and reduce the need for pesticides.
- Sequesters Carbon: Regenerative agriculture practices used to grow ROC Cotton aim to sequester carbon by increasing soil organic matter. This helps to reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere and mitigate the effects of climate change.
- Promotes Social Fairness: The Regenerative Organic Alliance certification for ROC Cotton includes requirements for social fairness, such as fair labor practices and fair wages for workers. This helps to ensure that the people involved in the production of ROC Cotton are treated fairly and ethically.
In comparison to organic cotton, ROC Cotton offers additional environmental benefits, such as increased soil health and biodiversity. While organic cotton is grown using organic practices, it does not necessarily promote regenerative agriculture practices. Therefore, ROC Cotton may have higher environmental benefits than organic cotton
How does regenerative organic certified cotton compare to other sustainable cotton options in terms of water usage?
Regenerative Organic Certified™ (ROC) Cotton is a sustainable cotton option that offers several environmental benefits. Here is how ROC Cotton compares to other sustainable cotton options in terms of water usage:
- Conventional Cotton: Cotton grown using conventional agricultural practices has significant environmental impacts, including high water usage. Conventional cotton requires a lot of water to grow, and it is estimated that it takes around 2,700 liters of water to produce one cotton t-shirt.
- Organic Cotton: Organic cotton requires less water than conventional cotton because it is grown using organic practices that eliminate the use of synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. However, the water usage for organic cotton can still vary depending on the region where it is grown.
- Recycled Cotton: Recycled cotton requires significantly less water than conventional or organic cotton because it is made from pre-consumer or post-consumer waste, such as fabric scraps or discarded clothing. The production of recycled cotton also avoids the water usage associated with growing new cotton.
- Cotton in Conversion: Cotton in Conversion, which comes from farmers who are transitioning their crops from conventional to organic cotton, may require more water than organic cotton because the transition process can be challenging and may require more water usage. However, the water usage for Cotton in Conversion can still vary depending on the region where it is grown.
- Regenerative Organic Certified™ (ROC) Cotton: ROC Cotton may require less water than organic cotton because regenerative agriculture practices used to grow ROC Cotton aim to improve soil health, which can help to retain water in the soil. However, the water usage for ROC Cotton can still vary depending on the region where it is grown.
In conclusion, while the water usage for each type of cotton can vary depending on the region where it is grown, recycled cotton and ROC Cotton are generally considered to be more sustainable options in terms of water usage than conventional and organic cotton.