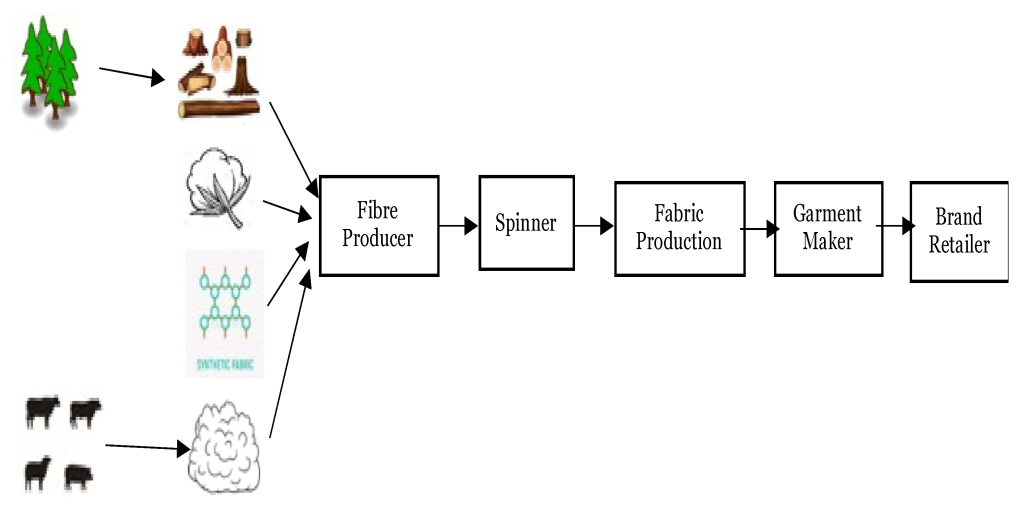
The textile and fashion industry faces challenges related to environmental pollution, human rights violations, counterfeit products, and lack of consumer trust. Achieving traceability and transparency is crucial to address these issues and ensure sustainability, quality, and accountability in the textile value chain.
Introduction
The textile and fashion industry is one of the most important sectors in the global economy. This industry generates over $2.5 trillion in annual revenue and employs over 60 million people worldwide. However, this industry also has a significant environmental and social impact, consuming large amounts of water, energy, and chemicals, generating huge amounts of waste and greenhouse gas emissions, and exposing workers to poor and unsafe working conditions.
In this context, traceability and transparency are essential for improving the efficiency, performance, and reputation of the textile supply chain.
Traceability refers to the ability to track the origin, history, and location of a product or its components throughout the supply chain.
Transparency refers to the ability to access and share relevant information about the product or its components, such as its environmental and social impact, quality standards, certifications, and authenticity.
Together, traceability and transparency can help:
-Reduce the risk of fraud, counterfeiting, and human rights violations by verifying the origin and authenticity of products3.
-Enhance the quality and safety of products by ensuring compliance with standards and regulations.
-Improve the efficiency and performance of the supply chain by optimizing production, inventory, and logistics processes.
-Increase consumer trust and loyalty by providing them with reliable and accessible information about the products they buy.
-Promote sustainability and circularity by encouraging responsible sourcing, production, consumption, and disposal of products.
The Importance of Traceability and Transparency in Textile Value Chain
Traceability and transparency are not only important for addressing the challenges faced by the textile industry but also for meeting the expectations of various stakeholders in the supply chain. These include:
For Consumers:
Consumers are becoming more aware of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions and are demanding more information about the products they buy. According to a survey by McKinsey & Company, 57% of consumers consider environmental or social impact as an important factor when buying clothing. Moreover, 75% of consumers say they would switch to a brand that provides more in-depth product information beyond what is on the physical label. Therefore, providing consumers with traceability and transparency can help increase their satisfaction, trust, loyalty, and willingness to pay for products.
For Brands:
Brands are facing increasing pressure from consumers, regulators, investors, NGOs, media, and competitors to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and social responsibility. According to a report by KPMG, 93% of the world’s largest 250 companies report on their sustainability performance. Moreover, 88% of CEOs say that sustainability is important for their business success. Therefore, providing traceability and transparency can help brands enhance their reputation, differentiate themselves from competitors, comply with regulations, attract investors, engage stakeholders, and drive innovation.
For Suppliers:
Suppliers are facing increasing challenges from brands to meet their requirements for quality, cost, speed, and sustainability. According to a survey by Accenture, 80% of suppliers say that sustainability is important for their business strategy. Moreover, 76% of suppliers say that they have experienced increased customer expectations for sustainability performance in the past three years. Therefore, providing traceability and transparency can help suppliers improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction, and create new business opportunities.
Challenges in Achieving Traceability and Transparency in Textile Value Chain
Despite the importance of traceability and transparency in the textile supply chain, achieving them is not easy. The current systems and methods for information sharing are often fragmented, inconsistent, incomplete, or inaccurate. Moreover, there are many barriers and challenges that hinder traceability and transparency, such as:
-The lack of common standards and protocols for data collection, exchange, and verification among different supply chain partners. This leads to difficulties in integrating and harmonizing data from various sources and platforms.
-The high cost and complexity of implementing traceability and transparency solutions across different platforms and systems. This requires significant investments in technology, infrastructure, and human resources.
-The reluctance or resistance of some supply chain partners to share sensitive or proprietary information due to competitive or legal reasons. This creates information asymmetry and mistrust among supply chain partners.
-The risk of data tampering, manipulation, or theft by malicious actors or intermediaries. This compromises the integrity, security, and reliability of data.
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Achieving Traceability & Transparency
Blockchain technology (BT) is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure and transparent transactions among multiple parties without the need for a central authority or intermediary. BT has several characteristics that make it attractive for traceability and transparency applications in the textile supply chain:
It is immutable: once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted by anyone. This ensures that data is accurate, consistent, and trustworthy.
It is verifiable: every transaction on the blockchain ledger can be validated by anyone using cryptographic methods. This ensures that data is authentic, complete, and compliant.
It is transparent: every transaction on the blockchain ledger can be viewed by anyone with access to the network. This ensures that data is accessible, shareable, and auditable.
It is decentralized: every transaction on the blockchain ledger is processed by a network of nodes that operate independently and collectively. This ensures that data is distributed, resilient, and scalable.
How blockchain technology can enhance traceability and transparency in the textile value chain?
By leveraging BT, traceability and transparency in the textile supply chain can be enhanced in several ways:
-It can create a single source of truth for product information across the supply chain, eliminating inconsistencies and discrepancies among different data sources. For example, Lenzing Group uses BT to trace its TENCEL™ branded fibers from wood sources to finished garments using digital certificates that are linked to the blockchain ledger.
-It can enable real-time tracking and tracing of products or their components throughout their lifecycle, from raw materials to end consumers. For example, TextileGenesis uses BT to trace natural fibers from fiber producers to brands using fibercoins™ that are linked to the blockchain ledger.
-It can provide proof of provenance, quality, authenticity, and sustainability of products or their components using digital certificates or tokens that are linked to the blockchain ledger. For example, Mastercard uses BT to help brands showcase their products’ origin, journey, and impact using Provenance Solution that is linked to the blockchain ledger.
-It can facilitate information sharing and collaboration among supply chain partners by creating smart contracts that automate transactions based on predefined rules and conditions. For example, IBM uses BT to help buyers verify their suppliers’ identity, capabilities, quality standards, certifications, etc using Trust Your Supplier platform that is linked to the blockchain ledger.
-It can increase consumer trust and engagement by providing them with access to verified product information via QR codes or mobile apps.
Examples of Blockchain Applications in Textile Value Chain
There are many examples of successful blockchain applications in the textile supply chain, such as follows:
Figure 1: Lenzing Group: a leading fiber producer that uses BT to trace its TENCEL™ branded fibers in textile value chain
Figure 2: TextileGenesis: a start-up company that developed a BT platform that uses fibercoins™ for traceability in textile value chain
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Technology
BT presents a promising solution that could transform the textile supply chain by facilitating traceability and transparency. However, there are still some challenges and limitations that need to be addressed before BT can be widely adopted in the textile industry. These include:
-The scalability and interoperability of BT platforms across different systems and networks.
-The standardization and regulation of BT protocols and data formats across different countries and regions.
-The education and awareness of supply chain partners and consumers about the benefits and risks of BT.
-The collaboration and coordination among supply chain partners to implement BT solutions effectively.
Therefore, it is important for all stakeholders in the textile industry to work together to explore the potential of BT in enhancing traceability and transparency in the textile supply chain.
References
https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/19/10496
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-69395-4_12