Cotton is one of the most widely used natural fibers in the textile industry, accounting for about 25 percent of the global fiber market. However, cotton production and consumption also face various social and environmental challenges, such as water scarcity, pesticide use, labor rights violations, and greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, cotton traceability, which is the ability to track the origin and journey of cotton through the supply chain, is becoming increasingly important for both the textile industry and the consumers.
Cotton traceability can help improve the sustainability, quality, and authenticity of cotton products, as well as enhance the transparency and accountability of the value chain actors. However, cotton traceability also faces some obstacles, such as the lack of standardized methods, technologies, and regulations across different regions and sectors. In this article, we will explore the different types of cotton traceability technologies that are available or in development, and compare their pros and cons for achieving a more sustainable and traceable cotton industry.
Common Cotton Traceability Technologies
There are different types of cotton traceability technologies that are available or in development, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common ones are:
DNA markers for cotton traceability:
These are molecular tags that are applied to the cotton fiber or seed and can be detected by a DNA test. They can provide a high level of accuracy and security, as they are unique and difficult to tamper with. However, they can also be costly, complex, and time-consuming to apply and verify.
Applied DNA Sciences is a company that offers DNA-based traceability solutions for a variety of industries, including the textile industry. Applied DNA Sciences’ technology uses a unique DNA marker that is attached to cotton fibers at the farm level. This marker can then be used to track the cotton through the supply chain and ensure that it is not being counterfeited or diverted.
Haelixa traceability technology is a solution that uses DNA-based molecular markers to track and verify the origin and authenticity of natural fibers, such as cotton, wool, cashmere, silk, etc., throughout the supply chain. The technology consists of two main components:
- DNA markers: These are unique molecular identifiers that are applied to the fibers at the source, such as the farm or the factory. The markers are designed to be durable, secure, and compatible with different types of fibers and processes. The markers can be detected at any point in the supply chain using forensic testing or on-site scanning.
- Haelixa platform: This is a software tool that collects, analyzes, and shares the data generated by the DNA markers. The platform provides visibility, traceability, and accountability of the fiber journey from source to shelf. The platform also enables communication and collaboration among the supply chain actors and stakeholders.
Isotopic analysis for cotton traceability:
This is a technique that measures the natural variations of stable isotopes in the cotton fiber, such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen. These isotopes can reflect the geographic origin and environmental conditions of the cotton growth. They can provide a low-cost and non-invasive method of verification, as they do not require any additional markers. However, they can also be affected by external factors, such as fertilizers, irrigation, and climate change.
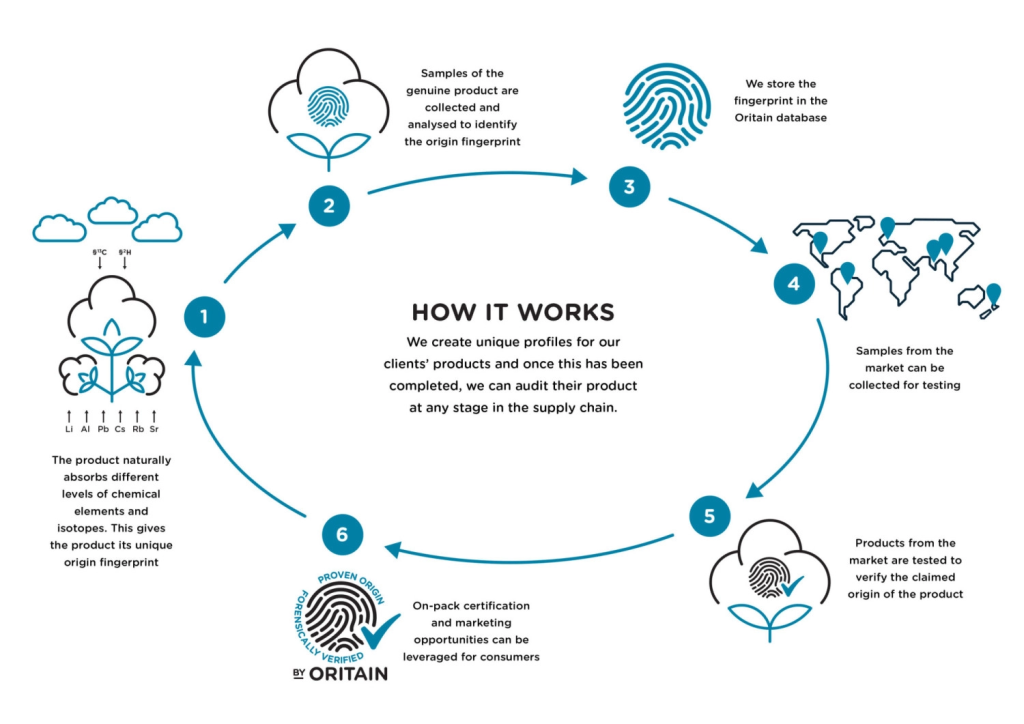
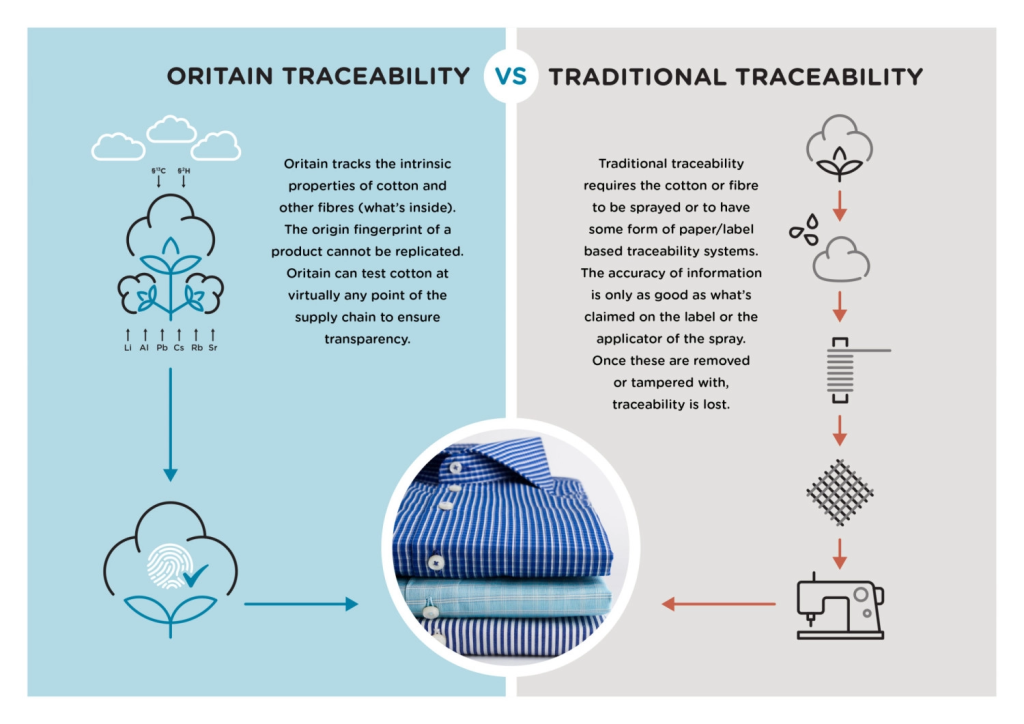
Oritain identifies products’ origin from ‘fingerprints’ derived from the chemical compositions of plants and animals, based on compound variations in the environment. They examine stable isotope ratios such as oxygen-18 to oxygen-16 and carbon-13 to carbon-12, and trace elements that occur in products, including essential elements and over 35 others. The method uses statistical models to determine a chemical fingerprint of origin and tests samples against it with a decision limit based on maximizing True Positive Rate and lowering False Negative Rate. Oritain adopts multiple processes to reduce error rates and ensure high correct classification of True Positives.
Blockchain for cotton traceability:
This is a digital ledger that records and stores transactions and data along the supply chain in a secure and decentralized way. It can provide a high level of transparency and traceability, as it allows all the stakeholders to access and verify the information. However, it can also be challenging to implement and scale, as it requires a common standard, a reliable network, and a strong governance.
The TextileGenesis traceability solution is a blockchain-based platform that allows brands to track the journey of their products from the farm to the consumer. TextileGenesis has some success stories with Lenznig, H&M, US Cotton, and Arvind.
The TextileGenesis traceability solution is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the textile industry. By providing a secure and transparent way to track the journey of products, the platform can help to make the textile industry more sustainable, ethical, and efficient.
Bext360 is a blockchain-based platform that is used to track the production of cotton. The platform uses a combination of satellite imagery, sensors, and blockchain technology to create a secure and tamper-proof record of the cotton’s journey from the farm to the consumer.
The Bext360 platform is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize the cotton industry. By providing a secure and transparent way to track the journey of cotton, the platform can help to make the cotton industry more sustainable, ethical, and efficient.
QR codes and RFID tags for cotton traceability:
These are physical labels that are attached to the cotton bales or products and can store information such as origin, quality, and certification. They can provide a low-cost and easy-to-use method of identification, as they can be scanned by a smartphone or a reader. However, they can also be vulnerable to fraud, damage, or loss.
| COTTON TRACEABILITY TECHNOLOGY | PROS | CONS |
| Permanent Bale Identification (PBI) tags | – Provide a unique and standardized identification for each U.S. cotton bale. – Allow textile mills to trace bales back to the gin and access their fiber quality data. – Can be combined with blockchain technology for enhanced security and transparency. | – Only applicable to U.S. cotton. – Do not provide information on the farm or field level. – Can be vulnerable to fraud, damage, or loss. |
| DNA Markers | – Provide a high level of accuracy and security, as they are unique and difficult to tamper with. – Can verify the origin and authenticity of the cotton fiber or seed. – Can be applied at any stage of the supply chain | – Costly, complex, and time-consuming to apply and verify. – Require specialized equipment and expertise. – Can be affected by environmental factors or processing methods |
| Isotopic Analysis | – Provide a low-cost and non-invasive method of verification, as they do not require any additional markers. – Can reflect the geographic origin and environmental conditions of the cotton growth. – Can be applied at any stage of the supply chain | – Affected by external factors, such as fertilizers, irrigation, and climate change. – Require specialized equipment and expertise. – Cannot verify the authenticity or integrity of the cotton fiber |
| Blockchain | – Provide a high level of transparency and traceability, as it allows all the stakeholders to access and verify the information. – Provide a secure and decentralized way of recording and storing transactions and data along the supply chain. – Can be combined with other traceability systems, such as PBI tags or DNA markers | – Challenging to implement and scale, as it requires a common standard, a reliable network, and a strong governance. – Costly and complex to maintain and operate. – Dependent on the quality and accuracy of the data input |
| QR Codes and RFID Tags | – Provide a low-cost and easy-to-use method of identification, as they can be scanned by a smartphone or a reader. – Can store information such as origin, quality, and certification. – Can be applied at any stage of the supply chain | – Vulnerable to fraud, damage, or loss. – Do not provide information on the fiber level. – Require a reliable network and database |
CottonConnect traceability solution is a software tool that uses a platform called TraceBale to track the cotton supply chain from farm to finished product. It is based on the following principles:
- Data gathering: CottonConnect collects data from farmers, ginners, spinners, knitters, weavers, and garment manufacturers at every stage of the cotton production and processing. The data includes information about the land, production, quality, quantity, and sustainability of the cotton and raw materials.
- Data verification: CottonConnect verifies the data using various methods, such as field visits, audits, third-party certifications, and blockchain technology. The verification ensures the accuracy and reliability of the data and the claims made by the supply chain actors.
- Data analysis: CottonConnect analyzes the data using various tools, such as dashboards, reports, and maps. The analysis provides insights into the performance, impact, and risks of the cotton supply chain and helps identify areas for improvement and innovation.
- Data sharing: CottonConnect shares the data with retailers and brands who use TraceBale to access their supply chain information. The data sharing enables transparency, traceability, and accountability of the cotton supply chain and helps communicate the sustainability story to customers and stakeholders.

Image from CottonConnect
Cottontrace traceability technology is a solution that uses a system of Permanent Bale Identification (PBI) tags to track and verify the origin and quality of U.S. cotton throughout the supply chain. The technology consists of two main components:
- PBI tags: These are unique identification numbers and barcodes that are assigned to every bale of U.S. cotton after it has been ginned. The tags are designed to be durable, secure, and compatible with different types of cotton and processes. The tags can be scanned at any point in the supply chain using electronic devices.
- Cottontrace platform: This is a software tool that collects, analyzes, and shares the data generated by the PBI tags. The platform provides visibility, traceability, and accountability of the cotton journey from gin to mill. The platform also enables communication and collaboration among the supply chain actors and stakeholders.
Example case studies
Some of the case studies or testimonials from brands or suppliers that have adopted or tested these technologies are:
Fashion for Good:
This is a global platform for innovation that aims to transform the fashion industry into a force for good. It has partnered with Bext360 and other technical partners to conduct a pilot project that uses on-product markers and blockchain technology to trace organic cotton from farm to retail. The pilot involved 75 metric tonnes of organic cotton from 13 farms in India and demonstrated the feasibility and scalability of the technology.
BASF:
This is a global company that provides agricultural solutions for various crops, including cotton. It has developed an e3 sustainable cotton program that uses Permanent Bale Identification (PBI) tags and blockchain technology to trace U.S. cotton from farm to consumer. The program also provides third-party verification and certification of the sustainability practices of the cotton farmers.
Haelixa:
This is a Swiss company that offers DNA-based traceability solutions for various materials, including cotton. It has partnered with WEBA, a textile manufacturer, to trace organic cotton from Tanzania and Egyptian cotton from Egypt using DNA markers. The project verified the origin and authenticity of the cotton throughout the supply chain.
Which cotton traceability technology is the best?
There is no definitive answer to which cotton traceability system is the best for your business, as it may depend on various factors, such as your budget, your customers’ preferences, your suppliers’ capabilities, and your sustainability goals.
DNA markers can provide a high level of accuracy and security, as they are unique and difficult to tamper with. They can verify the origin and authenticity of the cotton fiber or seed, which can help you ensure the quality and integrity of your products. They can also help you comply with the regulations and standards of the European and American markets, such as the EU Ecolabel or the U.S. Organic Cotton Standard.
Blockchain technology can provide a high level of transparency and traceability, as it allows all the stakeholders to access and verify the information. It can provide a secure and decentralized way of recording and storing transactions and data along the supply chain, which can help you improve your efficiency and accountability. It can also help you communicate your sustainability practices and impact to your customers and consumers, as well as enhance your reputation and trustworthiness.
A combination of DNA markers and blockchain technology can offer a comprehensive and robust traceability solution that can meet the diverse needs and preferences of the industry and the consumers. It can also leverage the strengths and overcome the weaknesses of each system, such as cost, complexity, scalability, and reliability.
What is the cost of cotton traceability technologies?
The cost of implementing a traceability system using DNA markers and blockchain technology may vary depending on various factors, such as the volume of cotton, the number of supply chain actors, the type and quality of the markers and the platform, and the frequency and scope of the verification. However, based on some web searches, some estimates that may give you an idea of the possible cost range:
According to a report by Fashion for Good, the cost of applying DNA markers to organic cotton in a pilot project was about $0.05 per kg of lint cotton. The cost of verifying the DNA markers at different stages of the supply chain was about $100 per sample. The cost of using blockchain technology to record and store the data was not specified, but it was expected to decrease over time as the technology matures and scales.
According to an article by Louis Dreyfus Company, the cost of applying DNA markers to Pima cotton in a commercial project was about $0.02 per pound of lint cotton. The cost of verifying the DNA markers at different stages of the supply chain was not specified, but it was mentioned that it was affordable and efficient. The cost of using blockchain technology to record and store the data was not specified either, but it was implied that it was included in the overall service fee.
According to an article by ETH Zurich, the cost of applying DNA markers to organic cotton in a pilot project was not specified, but it was stated that it was competitive and scalable. The cost of verifying the DNA markers at different stages of the supply chain was not specified either, but it was indicated that it was simple and fast. The cost of using blockchain technology to record and store the data was not specified, but it was suggested that it was secure and transparent.
Based on these estimates, one can say that the cost of implementing a traceability system using DNA markers and blockchain technology for cotton could range from $0.02 to $0.05 per kg or pound of lint cotton for applying the markers, and from $100 to $200 per sample for verifying the markers. The cost of using blockchain technology could vary depending on the platform and the service provider, but it could be lower than other traceability systems that require more infrastructure and maintenance.
Of course, these are just rough estimates based on limited information. You may want to contact some of the companies or organizations that offer these traceability solutions and get a more accurate quote based on your specific needs and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cotton traceability is a vital aspect of the textile industry and the consumers, as it can enhance the sustainability, quality, and authenticity of cotton products. However, cotton traceability also faces some challenges, such as the lack of standardized methods, technologies, and regulations across different regions and sectors. There are different types of cotton traceability technologies that are available or in development, such as DNA markers, isotopic analysis, blockchain, QR codes, and RFID tags. Each of these technologies has its own pros and cons, such as accuracy, cost, scalability, and security. Some of the brands and suppliers that have adopted or tested these technologies have shown positive results and feedback.
To improve cotton traceability in the future, some of the recommendations or suggestions are:
-To establish a common framework and standard for cotton traceability that can be adopted by all the stakeholders in the supply chain.
-To invest in research and innovation to develop more reliable, affordable, and scalable traceability technologies that can meet the diverse needs and preferences of the industry and the consumers.
-To increase the awareness and education of the consumers about the importance and benefits of cotton traceability and how they can access and verify the information.
References:
https://www.statista.com/topics/1542/cotton/
https://www.cottonworks.com/en/topics/sourcing-manufacturing/traceability/us-cotton-traceability/
https://www.onlineclothingstudy.com/2023/01/tracing-cotton-from-garment-to-farm.html
https://agriculture.basf.us/crop-protection/products/seeds/stoneville.html