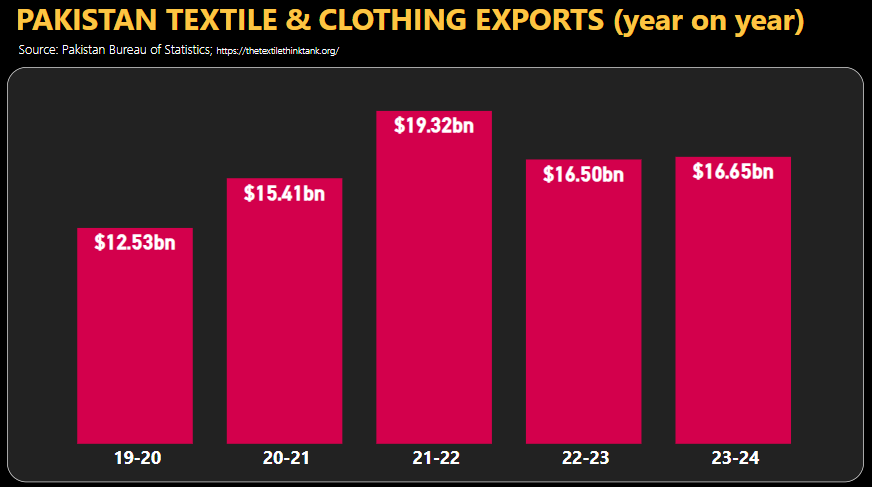
The textile and clothing sector in Pakistan has long been a cornerstone of the nation’s economy. The chart provides a year-on-year overview of the sector’s export performance from 2019-20 to 2023-24, highlighting significant trends and raising critical considerations for policy makers.
Data Source: PBS
Export Performance Analysis
- Steady Growth Post-Pandemic (2019-20 to 2021-22):
- 2019-20: The sector recorded exports worth $12.53 billion, reflecting a challenging period marked by global economic slowdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- 2020-21: There was a substantial recovery with exports increasing to $15.41 billion, demonstrating resilience and adaptability in the face of adversity.
- 2021-22: The peak of this period saw exports soaring to $19.32 billion, the highest in the last five years. This surge can be attributed to a robust global demand recovery, favorable government policies, and strategic market diversification.
- Decline in Exports (2022-23 and 2023-24):
- 2022-23: Exports fell to $16.50 billion, indicating a contraction of 14.6% from the previous year. This decline raises concerns about the sustainability of the export growth witnessed in the preceding years.
- 2023-24: A slight recovery to $16.65 billion suggests stabilization, but the figures remain significantly below the 2021-22 peak. This modest increase of 0.9% suggests that the sector is facing ongoing challenges.
Key Considerations for Policy Makers
- Market Diversification and Expansion:
- To mitigate the risks associated with over-reliance on a few markets, there is a need for strategic diversification. Exploring new markets in Africa, Latin America, Middle East, Russia and ASEAN countries could open up additional revenue streams.
- Enhancing Competitiveness:
- Addressing high energy cost issues, and investing in technology and innovation is critical to enhancing productivity and maintaining competitiveness in the global market. Policies aimed at upgrading machinery, adopting sustainable practices, and improving the skills of the workforce can provide a significant boost.
- Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions:
- The recent export decline highlights vulnerabilities in the supply chain. Developing resilient supply chain networks and investing in local increase raw material production can help reduce dependency on imports and enhance stability.
- Trade Policies and Incentives:
- Revisiting trade policies to provide more favorable conditions for exporters, such as tax incentives, subsidies, and easing regulatory hurdles, can stimulate growth. Additionally, negotiating better trade agreements with key partners could improve market access.
- Sustainable Practices:
- The global market is increasingly favoring sustainable and ethically produced goods. Adopting eco-friendly practices and obtaining relevant certifications can enhance the appeal of Pakistani textiles in international markets.
Conclusion
The fluctuating trend in Pakistan’s textile and clothing exports underscores the need for targeted policy interventions. By addressing the outlined challenges and leveraging the opportunities, policy makers can help stabilize and potentially grow this vital sector. Strategic initiatives focused on diversification, competitiveness, supply chain resilience, favorable trade policies, and sustainability will be pivotal in driving the future growth of Pakistan’s textile exports.



