The Waste Shipment Regulation (EU) 2024/1157, which replaces Regulation (EC) No 1013/2006, introduces stricter controls on waste exports, especially to non-OECD countries like Pakistan.
Pakistan is world’s largest importer of worn clothing in the world, with around 23% imports from EU, around 50% from US and the remaining from rest of the world.
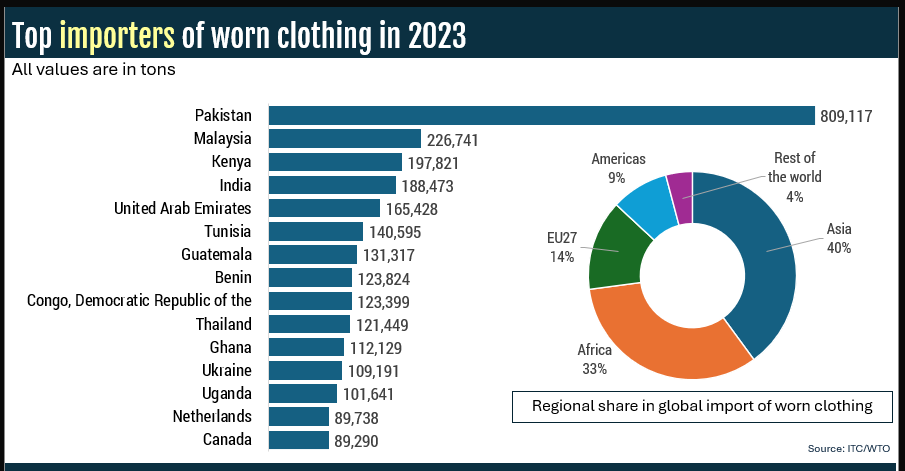
The key implications of textile waste exports from the EU to Pakistan are:
1. Stricter Controls on Waste Exports to Non-OECD Countries
- Implication: The EU aims to prevent waste dumping in third countries that lack the capacity for environmentally sound management (ESM).
- Impact on Pakistan:
- Textile waste imports from the EU will require strict environmental compliance and prove that Pakistan has the capacity to manage waste sustainably.
- Pakistan’s recycling sector may face higher compliance costs due to required audits and reporting.
2. Auditing and Certification Requirements for Waste Importers
- Implication: Before exporting textile waste, EU exporters must conduct independent third-party audits of Pakistani recycling facilities.
- Impact on Pakistan:
- Textile recycling units in Pakistan must undergo environmental audits to continue receiving EU textile waste.
- Small-scale recyclers may struggle to meet the EU’s auditing standards, reducing the number of compliant facilities.
3. Ban on Exports of Certain Waste Categories
- Implication: The EU is banning exports of hazardous and hard-to-recycle waste, including some textile waste.
- Impact on Pakistan:
- Pakistan may lose access to certain textile waste streams, affecting industries that rely on EU textile scrap.
- Risk of illegal shipments increases if waste exporters try to bypass restrictions.
4. Focus on Circular Economy and Local Processing
- Implication: The EU is prioritizing waste recycling within the EU instead of exporting waste to third countries.
- Impact on Pakistan:
- Reduced availability of textile waste from the EU might impact Pakistan’s recycled textile industry, which depends on imported textile waste.
- Pakistan may need to increase local textile waste recycling to offset the reduced imports.
5. Compliance with International Labour and Environmental Standards
- Implication: The EU will only export textile waste to countries that meet labour rights and environmental sustainability criteria.
- Impact on Pakistan:
- Pakistani textile waste processors must comply with global labour and environmental standards (e.g., ILO conventions).
- Non-compliance could lead to suspension of waste shipments to Pakistan.
6. Potential Opportunities for Pakistan
While the regulation imposes stricter compliance, it also presents opportunities for Pakistan:
- Investment in Green Textile Recycling
- Pakistani firms can attract foreign investment to upgrade waste processing facilities.
- Compliance with EU standards could enhance Pakistan’s position as a sustainable textile recycler.
- Boost to Local Circular Economy
- With reduced imports, Pakistan can focus on local textile waste collection and recycling.
- Encourages development of a domestic circular textile economy aligned with global sustainability trends.
- Stronger EU-Pakistan Trade Relations
- Compliance with EU waste regulations could improve Pakistan’s reputation as a responsible trade partner.
- May lead to preferential access to sustainable textile supply chains in Europe.
Roadmap for Compliance with the EU Waste Shipment Regulation (2024/1157) for Textile Waste Imports into Pakistan
This roadmap outlines key actions Pakistan’s textile recycling industry, policymakers, and businesses must take to align with the EU’s new waste export restrictions and maintain access to EU textile waste imports.
1️⃣ Immediate Actions (0-6 Months) – Understanding & Legal Compliance
Objective: Ensure awareness and initial alignment with EU regulations.
✅ Step 1: Awareness and Stakeholder Engagement
- Conduct awareness sessions for textile recyclers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders about the new EU Waste Shipment Regulation (2024/1157).
- Engage with the Pakistan Textile Exporters Association (PTEA) and Pakistan Recycling Industry stakeholders to discuss regulatory impacts.
- Establish a Government-Industry Task Force to monitor compliance progress.
✅ Step 2: Policy Review and Legal Alignment
- Align Pakistan’s waste import policies with the EU’s new requirements.
- Update waste import licensing to include EU-mandated sustainability and audit standards.
- Strengthen environmental laws related to textile waste management, incorporating Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) policies.
✅ Step 3: Develop a Certification & Audit Framework
- Work with the Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency (Pak-EPA) to create a national certification system for textile waste recyclers.
- Ensure facilities meet EU’s Environmental and Social Management System (ESMS) standards.
- Collaborate with international auditors for third-party certification of compliant recycling units.
2️⃣ Short-Term Actions (6-12 Months) – Facility Upgradation & Certification
Objective: Upgrade Pakistan’s recycling infrastructure to meet EU sustainability standards.
✅ Step 4: Facility Upgradation for Environmental Standards
- Require textile waste recycling firms to adopt cleaner production methods, wastewater treatment, and air emission control.
- Implement waste tracking and monitoring systems to prevent illegal waste dumping.
- Encourage investment in mechanical and chemical textile recycling technologies.
✅ Step 5: Implement Third-Party Audits & Compliance Checks
- Identify and certify priority recycling firms that meet EU’s waste handling standards.
- Conduct pilot audits with EU-approved third-party certification agencies (e.g., SGS, TÜV, Bureau Veritas).
- Ensure social compliance with labor laws, banning forced and child labor in textile waste processing.
✅ Step 6: Improve Supply Chain Traceability & Transparency
- Develop a national waste tracking database to digitally document imported textile waste movements.
- Promote adoption of Digital Product Passport (DPP) technologies for traceability in textile waste processing.
- Establish a Pakistan Textile Waste Monitoring System (PTWMS) to ensure EU transparency requirements are met.
3️⃣ Medium-Term Actions (1-3 Years) – Market Diversification & Circular Economy
Objective: Build a sustainable textile waste ecosystem in Pakistan, reducing reliance on EU imports.
✅ Step 7: Attract Investment in Circular Textile Economy
- Develop Textile Waste Processing Zones (TWZs) in Lahore, Karachi, and Faisalabad to centralize waste recycling.
- Offer tax incentives for green textile recycling investments.
- Engage with European investors to build local fiber-to-fiber recycling plants.
✅ Step 8: Strengthen Local Textile Waste Collection & Recycling
- Launch a domestic textile waste collection program to reduce dependence on EU waste imports.
- Introduce waste segregation laws to encourage local post-consumer textile recycling.
- Develop Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for circular economy projects.
✅ Step 9: Establish Trade Agreements with the EU
- Negotiate a “Green Textile Waste Partnership” with the EU to ensure Pakistan remains an approved waste importer.
- Align with Pakistan-EU GSP+ criteria to strengthen trade in sustainable textiles.
- Promote Pakistan’s role as a responsible circular textile hub through participation in international sustainability conferences.
4️⃣ Long-Term Actions (3+ Years) – Global Leadership in Sustainable Textiles
Objective: Position Pakistan as a leading global hub for sustainable textile waste processing.
✅ Step 10: Develop Pakistan’s Own Circular Textile Strategy
- Implement a National Circular Textile Policy to make textile waste recycling a long-term economic sector.
- Establish Pakistan’s own end-of-waste criteria to certify high-quality recycled fibers for global markets.
- Promote exports of recycled textiles and fibers as Pakistan’s new competitive advantage.
✅ Step 11: Advance Green Innovation in Textile Recycling
- Set up Textile Circular Economy Research Centers in collaboration with universities.
- Promote research on textile-to-textile recycling, biodegradable fibers, and non-toxic dyes.
- Adopt blockchain technology for full textile traceability and anti-greenwashing measures.
✅ Step 12: Strengthen Global Collaboration
- Partner with EU’s Horizon Europe programs to access funding for circular textile initiatives.
- Work with global organizations like UNEP, GIZ, and WWF to enhance circular textile practices.
- Expand partnerships with international brands (H&M, Adidas, Levi’s) looking for ethical and sustainable waste recycling partners.
Detailed Policy Reforms, Investment Strategies, and Sector-Specific Implementation Plans for Textile Waste Imports from the EU
To ensure compliance with the EU Waste Shipment Regulation (2024/1157) and strengthen Pakistan’s position as a leader in sustainable textile waste processing, a three-pronged approach is required:
- Policy and Regulatory Reforms 🏛
- Investment and Infrastructure Development 💰
- Sector-Specific Implementation Plan 🏭
1️⃣ Policy and Regulatory Reforms 🏛
Objective: Align Pakistan’s waste management and textile recycling regulations with EU sustainability standards to maintain access to EU textile waste imports.
| Reform Area | Recommended Actions | Lead Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Import Regulations | – Update Pakistan’s Import Policy Order to align with the EU’s waste categorization and auditing requirements. | Ministry of Commerce, FBR, Pakistan Customs |
| Environmental Standards | – Strengthen Pakistan Environmental Protection Act (PEPA) 1997 to include textile waste recycling guidelines. | Pak-EPA, Ministry of Climate Change |
| Waste Traceability | – Implement a digital tracking system for imported textile waste shipments (blockchain-based traceability). | Pakistan Customs, Textile Industry Associations |
| Circular Economy Legislation | – Introduce Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws for local textile manufacturers. | Ministry of Industries, Pak-EPA |
| Trade Policy Adjustments | – Establish a Pakistan-EU Sustainable Trade Agreement for continuous textile waste flow. | Ministry of Commerce, Trade Development Authority |
📌 Key Outcome: A legal and regulatory framework that meets EU’s compliance and traceability requirements.
2️⃣ Investment and Infrastructure Development 💰
Objective: Attract local and foreign investment to develop a world-class textile waste recycling ecosystem in Pakistan.
| Investment Focus | Recommended Actions | Potential Investors/Partners |
|---|---|---|
| Textile Waste Recycling Zones (TWRZs) | – Establish dedicated recycling hubs in Lahore, Karachi, and Faisalabad with tax-free incentives. | SEZ Authorities, Board of Investment |
| Waste-to-Resource Processing Plants | – Develop fiber-to-fiber recycling plants for converting waste textiles into reusable raw materials. | Private investors, Foreign brands |
| Green Financing & Subsidies | – Offer low-interest green loans and tax exemptions for sustainable textile recycling projects. | SBP, IFC, ADB, European Development Bank |
| Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) | – Facilitate PPPs with EU brands to develop joint waste recycling programs. | H&M, Zara, Adidas, Levi’s, GIZ |
📌 Key Outcome: A modern recycling infrastructure that meets EU sustainability standards and reduces reliance on imported waste.
3️⃣ Sector-Specific Implementation Plan 🏭
Objective: Ensure Pakistan’s textile recycling industry adapts to EU’s requirements while maximizing economic and sustainability benefits.
A. Textile Recycling Industry Readiness
| Implementation Area | Key Actions | Responsible Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| Facility Certification | – Implement third-party certification for recycling plants (ISO 14001, EU-approved auditors). | Pak-EPA, EU Certifiers (SGS, TÜV) |
| ESG Compliance | – Develop Environmental & Social Governance (ESG) criteria for textile recycling facilities. | SECP, Textile Industry Associations |
| Labour Standards Enforcement | – Ensure no forced/child labor in textile waste processing. | Labour Ministry, ILO, GIZ |
📌 Key Outcome: Certified textile recycling facilities that meet EU’s sustainability and labor requirements.
B. Enhancing Traceability & Transparency
| Implementation Area | Key Actions | Responsible Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Traceability System | – Launch Pakistan Textile Waste Monitoring System (PTWMS) for real-time tracking. | Ministry of Commerce, Customs |
| Blockchain-Based Tracking | – Implement Digital Product Passports (DPP) for tracking textile waste origins. | Textile Exporters, EU Partners |
| Reporting & Audits | – Require annual sustainability reporting from textile recyclers. | Pakistan Stock Exchange (PSX), SECP |
📌 Key Outcome: A transparent, EU-compliant tracking system that ensures responsible waste handling.
C. Local Textile Waste Collection & Recycling
| Implementation Area | Key Actions | Responsible Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| Textile Waste Collection | – Develop municipal waste collection centers for textile waste. | Local Governments, Waste Companies |
| Sorting & Processing Units | – Establish sorting plants to segregate textile waste before recycling. | Textile Industry, SMEs |
| Public Awareness Campaigns | – Educate brands and consumers on recycling and circular fashion. | Ministry of Information, NGOs |
📌 Key Outcome: Boosts domestic textile waste recycling, reducing reliance on EU waste imports.
D. Green Trade and Export Strategy
| Implementation Area | Key Actions | Responsible Agencies |
|---|---|---|
| Pakistan-EU Sustainable Trade Agreement | – Negotiate long-term EU textile waste import/export partnerships. | Ministry of Commerce, EU Delegation |
| Export of Recycled Textiles | – Establish Pakistan as a supplier of certified recycled textile fibers. | Trade Development Authority, TDAP |
| EU CBAM Compliance | – Reduce carbon footprint in textile waste recycling to avoid tariffs. | Ministry of Climate Change, FBR |
📌 Key Outcome: Sustainable export growth, ensuring Pakistan remains a trusted EU partner.
1️⃣ Policy Reform Priorities
✅ Enforce Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) laws for textile manufacturers.
✅ Adopt EU’s “End-of-Waste” criteria for certifying high-quality recycled fibers.
✅ Strengthen textile waste import laws to prevent illegal shipments.
2️⃣ Investment and Industrial Upgradation
✅ Develop Pakistan’s first Textile Recycling Economic Zone (TREZ).
✅ Encourage foreign direct investment (FDI) in green textile processing.
✅ Support SMEs in textile waste upcycling.
3️⃣ Compliance with EU Regulations
✅ Implement Digital Product Passport (DPP) tracking.
✅ Adopt ISO 14001 sustainability standards for textile recycling.
✅ Create a formal Pakistan-EU Circular Textile Partnership.
🚀 The Opportunity for Pakistan
By following this roadmap, Pakistan can: ✅ Maintain access to EU textile waste imports under the new Waste Shipment Regulation (2024/1157).
✅ Position itself as a global leader in circular textiles.
✅ Create new economic opportunities in green trade and recycling.
Detailed Action Plan for Compliance with EU Waste Shipment Regulation (2024/1157) & Strengthening Pakistan’s Circular Textile Industry
This action plan provides step-by-step implementation strategies for government agencies, private sector stakeholders, and international partners to ensure Pakistan’s continued access to EU textile waste imports and its transition into a global leader in circular textiles.
1️⃣ Action Plan for Government Agencies 🏛
Objective: Align Pakistan’s waste management, trade, and environmental policies with EU’s circular economy and waste regulations.
| Action Area | Key Steps | Responsible Agencies | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Update Waste Import Laws | – Amend Pakistan’s Import Policy Order to include EU waste categorization & compliance standards. | Ministry of Commerce, FBR, Pakistan Customs | 6 months |
| Enforce Waste Recycling Certification | – Implement a Pakistan Textile Waste Certification Program (PTWCP) aligned with EU sustainability. | Pakistan Environmental Protection Agency (Pak-EPA) | 12 months |
| Develop Circular Textile Policy | – Introduce Pakistan’s Circular Textile Policy (PCTP) to regulate and incentivize textile recycling. | Ministry of Climate Change, TDAP, Textile Ministry | 18 months |
| Introduce Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) | – Require textile manufacturers to take responsibility for waste collection & recycling. | Ministry of Industries, SECP, Textile Industry Associations | 12 months |
| Implement Digital Traceability System | – Establish a blockchain-based waste tracking system for textile waste imports. | Pakistan Customs, Textile Exporters, EU Partners | 24 months |
📌 Outcome: Pakistan’s policies will align with EU sustainability standards, ensuring a continuous flow of textile waste imports from the EU.
2️⃣ Action Plan for Private Sector 🏭
Objective: Upgrade Pakistan’s textile waste recycling industry to meet EU sustainability and transparency requirements.
| Action Area | Key Steps | Responsible Private Stakeholders | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Upgrade Textile Recycling Facilities | – Invest in fiber-to-fiber recycling to meet EU circular economy standards. | Large textile recyclers, industrial units | 12-24 months |
| Obtain EU-Recognized Certifications | – Ensure compliance with ISO 14001, GOTS, and EU waste processing certifications. | Textile Recycling Units, SGS, TÜV | 12 months |
| Implement Supply Chain Traceability | – Adopt Digital Product Passports (DPP) to track textile waste origins. | Major exporters, brands, software providers | 24 months |
| Reduce Carbon Footprint for CBAM | – Install renewable energy & waste-to-energy technologies in recycling plants. | Energy-efficient recyclers, factories | 36 months |
| Develop Local Textile Waste Collection | – Set up municipal collection programs to increase domestic textile waste recycling. | Recycling companies, SMEs, Local NGOs | 12 months |
📌 Outcome: Pakistan’s textile recyclers will be certified & transparent, ensuring they can continue importing waste textiles under EU regulations.
3️⃣ Action Plan for International Collaboration 🌍
Objective: Strengthen EU-Pakistan partnerships in sustainable textile waste management and attract green investments.
| Collaboration Area | Key Steps | International Partners | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pakistan-EU Sustainable Textile Trade Agreement | – Sign a formal EU-Pakistan Green Textile Waste Partnership to ensure compliance. | EU Trade Delegation, Ministry of Commerce | 24 months |
| Green Finance & Foreign Investment | – Secure grants and green loans from EU sustainability programs. | EU Investment Banks, IFC, ADB, GIZ | 18 months |
| Knowledge & Technology Transfer | – Partner with European firms for advanced textile waste-to-resource processing. | Circular Economy Research Institutions | 36 months |
| Capacity Building for Recyclers | – Train Pakistani recyclers on EU textile waste handling best practices. | UNIDO, GIZ, International Textile Federations | 12 months |
| Sustainability Certification Support | – EU to assist Pakistan in fast-tracking compliance with EU certification standards. | EU Sustainability & Trade Bodies | 12-24 months |
📌 Outcome: Pakistan will establish strong partnerships with EU institutions, making it a preferred textile waste recycling destination.
4️⃣ Action Plan for Infrastructure Development & Investment 💰
Objective: Develop Pakistan’s circular textile ecosystem through investment in waste processing zones & green textile production.
| Investment Area | Key Steps | Responsible Agencies | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|
| Develop Textile Waste Processing Zones | – Establish Textile Recycling Economic Zones (TREZs) in Karachi, Lahore, Faisalabad. | Board of Investment, Industrial Estates | 24 months |
| Incentivize Circular Textile Businesses | – Offer tax breaks & subsidies to companies using recycled fibers. | Ministry of Finance, BOI | 12 months |
| Fund Circular Textile R&D | – Set up a Green Textile Research Center to develop sustainable fiber technologies. | Higher Education Commission (HEC), ADB | 36 months |
| Support SMEs in Textile Recycling | – Provide low-interest green loans for small recyclers to upgrade facilities. | State Bank of Pakistan (SBP), SECP | 18 months |
| Develop Local Waste Collection Systems | – Launch PPP-driven textile waste collection systems to reduce dependency on EU waste. | Textile Associations, Private Investors | 12 months |
📌 Outcome: Pakistan will develop world-class textile waste recycling infrastructure, ensuring long-term sustainability & economic benefits.
📌 Key Milestones & Timeline Overview 🗓
| Timeframe | Key Milestone |
|---|---|
| 0-6 Months | Update Pakistan’s Import Policy Order to align with EU waste shipment rules. |
| 6-12 Months | Launch Pakistan Textile Waste Certification Program (PTWCP). |
| 12-18 Months | Upgrade major textile recycling facilities & ensure EU-compliant audits. |
| 18-24 Months | Implement Digital Product Passports (DPP) & waste traceability systems. |
| 24-36 Months | Develop Pakistan’s first Textile Recycling Economic Zone (TREZ). |
| 36+ Months | Position Pakistan as a regional leader in circular textile waste processing. |
🎯 Expected Benefits for Pakistan
✅ Continued access to EU textile waste imports despite new restrictions.
✅ Boosted FDI & green financing for Pakistan’s textile recycling industry.
✅ Strengthened Pakistan’s textile exports under the EU GSP+ scheme.
✅ Reduced reliance on imported textile waste through local waste collection & circular economy policies.
✅ Global recognition as a leader in sustainable textiles.



